3
62
History
Sculpture
Like its architecture, Ancient Egyptian sculpture was created for religious and funerary
purposes.
This is illustrated by the following characteristics:
❚
The bodies were rigid and without movement.
❚
The faces showed no emotion and the figures appeared impassive.
❚
The most important figures, such as gods and pharaohs, were larger than the
others. The more important they were, the larger they were.
For scenes of everyday life, they used less valuable materials, like clay or wood. These
were depicted in a more natural way.
The majority of Egyptian sculpture was freestanding, that is, it was not incorporated
into the walls of buildings, although reliefs were also used in temples.
Painting
Painting in ancient Egypt was used to
decorate palaces, temples and tombs.
It was also used on papyrus to illustrate
sacred books.
The main characteristics were the use of
flat colours (without variations of tone,
shading, or volume); outlines of figures
and the difference in the size of the
figures, depending on the importance of
the person represented.
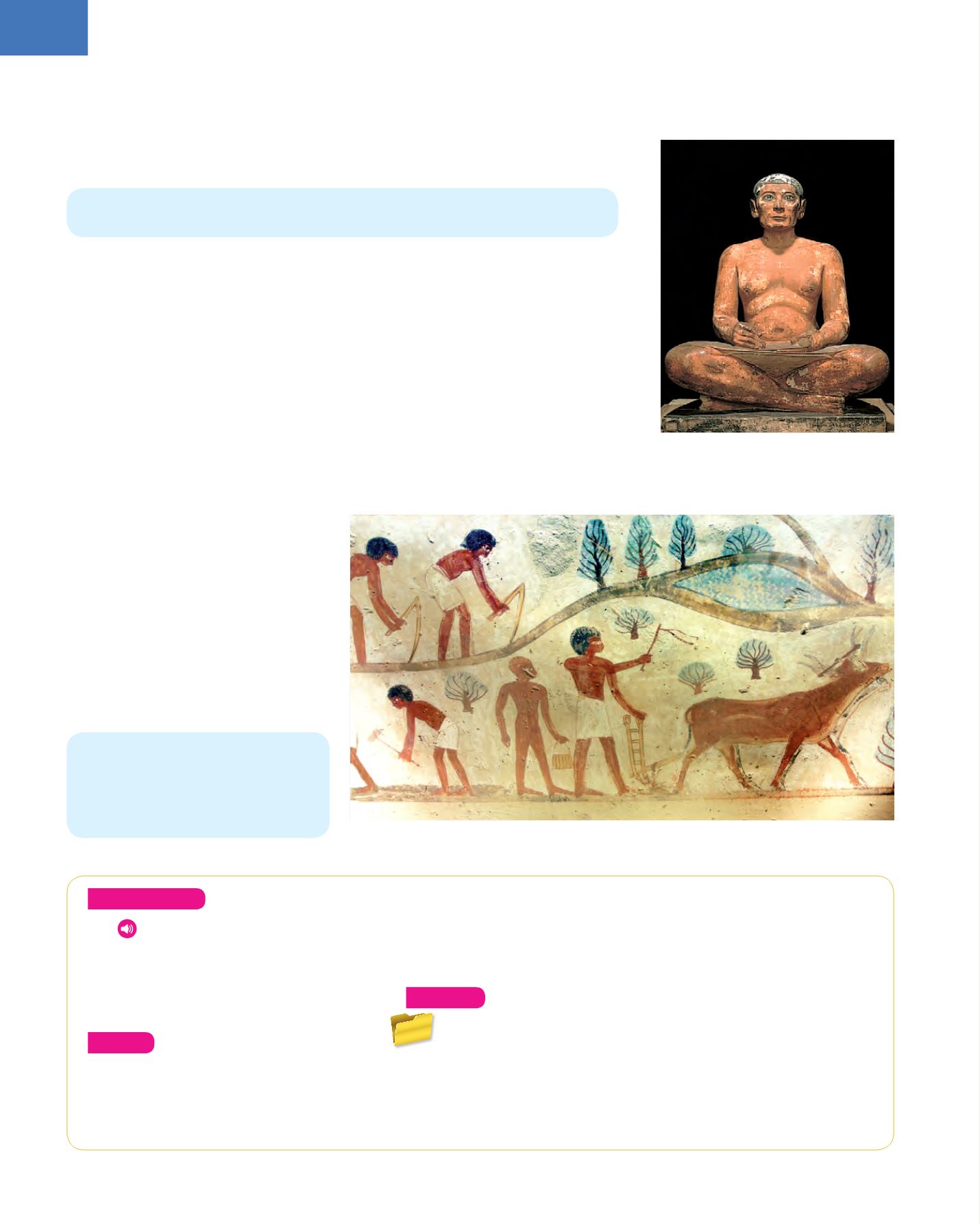
The Seated Scribe
, sculpture from the Old
Kingdom (Louvre Museum, Paris)
Agricultural tasks. Decoration from the tomb of an Egyptian noble (Luxor)
The most important works were made of
stone.
The figures adopted unnatural
positions to reflect their greatness and
solemnity.
The most important characteristic of
Egyptian painting is the
canon of
profile
. The limbs and face are drawn
in profile, but the torso and one eye
are depicted from the front view.
Understand
38.
Listen and say true or false. Correct
the false sentences.
39.
Explain
the
profile
painting
technique. What were the other main
characteristics of Egyptian painting?
Apply
40.
In your notebook, draw diagrams of the
four types of funeral constructions. Label
the main parts of each of these buildings
and write a brief description of them.
41.
Write a summary of the similarities and differences between
The Seated Scribe
and the sculptures at the entrance to the
tomb of Ramesses II, on page 230.
Create
42.
Find out about the curse of Tutankhamun. Try to find a logical
explanation for the deaths related to curse.
43.
How were the Ancient Egyptians able to move the great blocks
of stone and construct the pyramids if the wheel hadn´t been
invented yet?


