3
The Geosphere
118
4.
The use of rocks
Ask the students:
What objects can you see around you that are
made of rocks?
Probably they will find objects related to building.
However, rocks are useful in the majority of objects around us,
from building to technological ones.
Read the following sentences just to review some types of rocks
that will be useful during the lesson:
❚
Granite and basalt are igneous or magmatic rocks.
❚
Limestone, clay, coal and petroleum are sedimentary rocks.
❚
Marble and slate are metamorphic rocks.
Human beings have been using rocks since the Palaeolithic
Age. At the beginning their use was natural, such as refuges
(caves or caverns) or utensils for hunting. Nowadays, the
main use of rocks is for building, ornamentation, and as a
source of fuels and technological materials. In the latter, they
do not use rocks directly to produce them, but rather minerals
extracted from them like aluminum, which is obtained from
bauxite.
Now, students should do questions 28 to 30. 28. Ask students to
do this in their notebooks and then compare with another stu-
dent. 29. Do this as a whole class activity, eliciting the answer. 30.
Write different possibilities on the board and then ask students to
choose the most appropriate answer for each.
Review concepts learnt in this section by reading the
Key
concepts
on page 60.
Curricular adaptation:
7. THE USE OF ROCKS
Section adapted according to the curriculum.
5.
Extraction of minerals and rocks
This section could make students think about the importance of
sustainable management of mineral and rock resources. It is es-
sential to know the consequences of the uncontrolled use of tho-
se resources, both for the environment and for people.
It is important that students become aware of the need for sear-
ching for alternatives to use and overuse of non-renewable re-
sources as well as their consequences. Sustainable use of mineral
and rock resources allow better work conditions for millions of
people and also avoid unnecessary risks. Now students do ques-
tions 31 and 32.
Tips: 31. Ask students to look at the different definitions of ex-
traction and the image. 32. Elicit different answers from the class.
Web page:
THE PROCESS OF GOLD EXTRACTION
AND ITS USE
To finish this section, students could watch this video. It is about
the extraction of gold and its importance to humans. After
watching the video, answer the questions on the worksheet.
Curricular adaptation:
8. MINERAL AND ROCK
EXTRACTION
Section adapted according to the curriculum.
60
61
3. Thegeosphere
3
+
www
4.
THE USE OF ROCKS
The evolution of humans since the Palaeolithic Age has been linked to the use
of rocks for building, ornamentation or making utensils for hunting. Today, we
continue to use rocks for these activities.
The main uses of rocks are building, ornamentation and as a source of fuels and
technological materials.
❚
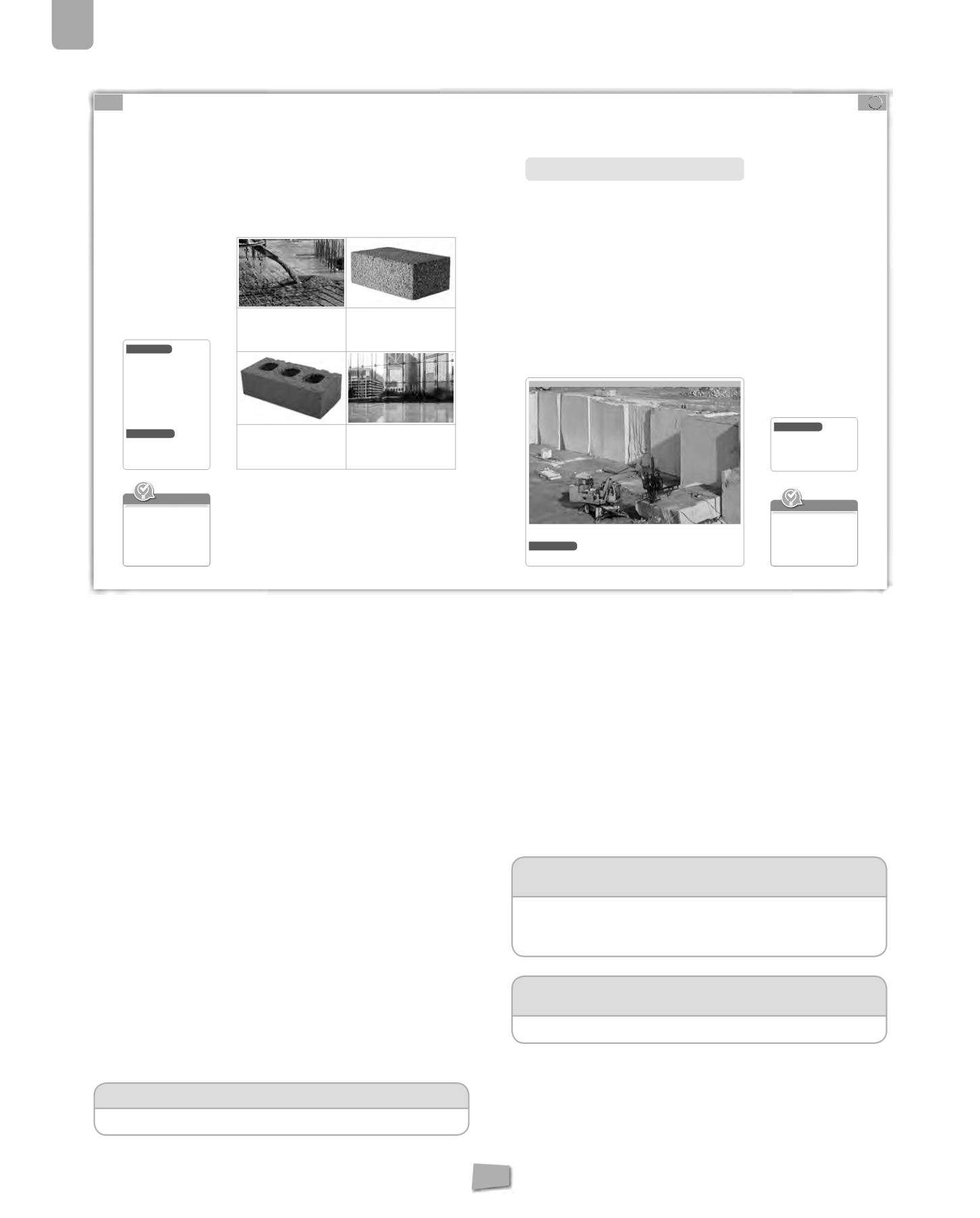
Building materials
: some rocks are used directly. Others are modified for
building purposes.
Cement,concrete,ceramicsandglassare someofmostcommonlyusedbuilding
materials. They all come from rocks.
5.
EXTRACTION OF MINERALS AND ROCKS
Rocks and minerals are extracted from mineral deposits in the Earth’s crust.
Theminerals thatareof interest toextractarecalled
oredeposit
.Theother rocksand
mineralsare referred toas
gangue
.
To locate a deposit
drill holes
are made with large drills. Cylinders of earth are
extracted and then analysed.
Depending on how deep a deposit is and its accessibility, the extraction can be
superficial or subterranean.
❚
Superficial extractions
: rocks and minerals are extracted from the surface or
notverydeepunder the surface.This typeofextractionhasagreat impacton the
environment. There are various types:
•
In
opencast mines
, such as those in Riotinto (Huelva), the minerals are not
deep underground. To extract them, they make funnel-shaped holes (pits). The
edges are stepped to transport the minerals to the surface.
•
In
quarries
, large rocks are extracted, cut into blocks or slabs. An example are
the marble quarries in Macael (Almería).
•
Gravel
4
is extracted from
gravel pits
. These are usually found in or near large
riverbeds. There are many in the Tajo river basin.
❚
Subterranean extractions
: rocks and minerals are located deep within the crust
and are extracted using
underground mines
. Vertical tunnels called shafts are
constructedandhorizontal tunnelsorgalleriescalled
adits
, toextract theminerals.
Key concepts
❚
A deposit is the place
where minerals or rocks are
extracted.
❚
Extractions are classified
according
to
depth:
superficial or subterranean.
A
deposit
is the place where minerals or rocks are found in sufficient quantity
to make extraction economically beneficial.
Key concepts
❚
Rocks are used, directly
or modified, as building
materials.
❚
Rocks also have ornamental
uses, as fossil fuels or as
a source of minerals for
technological use.
Cement
is obtained by grinding and
heating limestone and clay. It is mixed
with water to create a substance that
hardens
3
when dry. It allows us to stick
rocks together.
Concrete
is created by mixing cement,
water, sand and gravel. When dry, it
is harder and stronger than cement.
This is why it is used for pillars and
foundations.
Ceramics
are made with pulverised
clay mixed with water, modelled and
cooked at high temperatures.
They are used to make bricks, tiles
or dishes.
Glass
is created from quartz present
in sand. Sand is placed in an oven at a
high temperature and it melts. When
cooled, glass can be shaped in different
ways.
3
harden:
to become hard
Extractionof rocks
Understand
31.
What type of superficial extraction is shown in the picture?
❚
Ornamentalrocks
:marble,granite,slateandbasaltareoftenused indecoration.
Due to their beauty once they have been carved and polished, these rocks are
used in sculptures, floors of buildings and many other decorative elements in the
interior and exterior of buildings.
❚
Source of fossil fuels
: sedimentary rocks such as coal and oil are used because
they produce a lot of when burnt.
❚
Source of minerals for technological use
: rocks rich in quartz are a source of
silicon, which is used to make computer processors or photovoltaic solar panels.
Aluminium, obtained from a sedimentary rock called bauxite, is used to make
many objects such as planes, soft drink cans or kitchen utensils.
Remember
28.
Make a table of rocks
used to make building
materials. Include what
materials they are used
to make and the uses of
those materials.
29.
Which types of rocks
are usually used for
decoration?
Understand
30.
Explain the difference
between concrete and
cement.
Understand
32.
Explain in your own
words, the difference
betweenasubterranean
mine and a quarry.
4
gravel:
amixtureof rock fragments
between2and64mm


