3
The Geosphere
130
EXAM B
1.
Indicate the similarities and differences between
opencast mines and underground mines.
They are both mines to extract minerals. In opencast mines,
minerals are extracted from the surface or hot very deep
under the surface while in underground mines they make
funnel-shaped holes called pits to extract the minerals.
2.
Match the following minerals to their hardness:
Very hard
Diamond
Gypsum
Hard
Topaz
Apatite
Soft
Talc
Quartz
Very soft
Orthoclase
Calcite
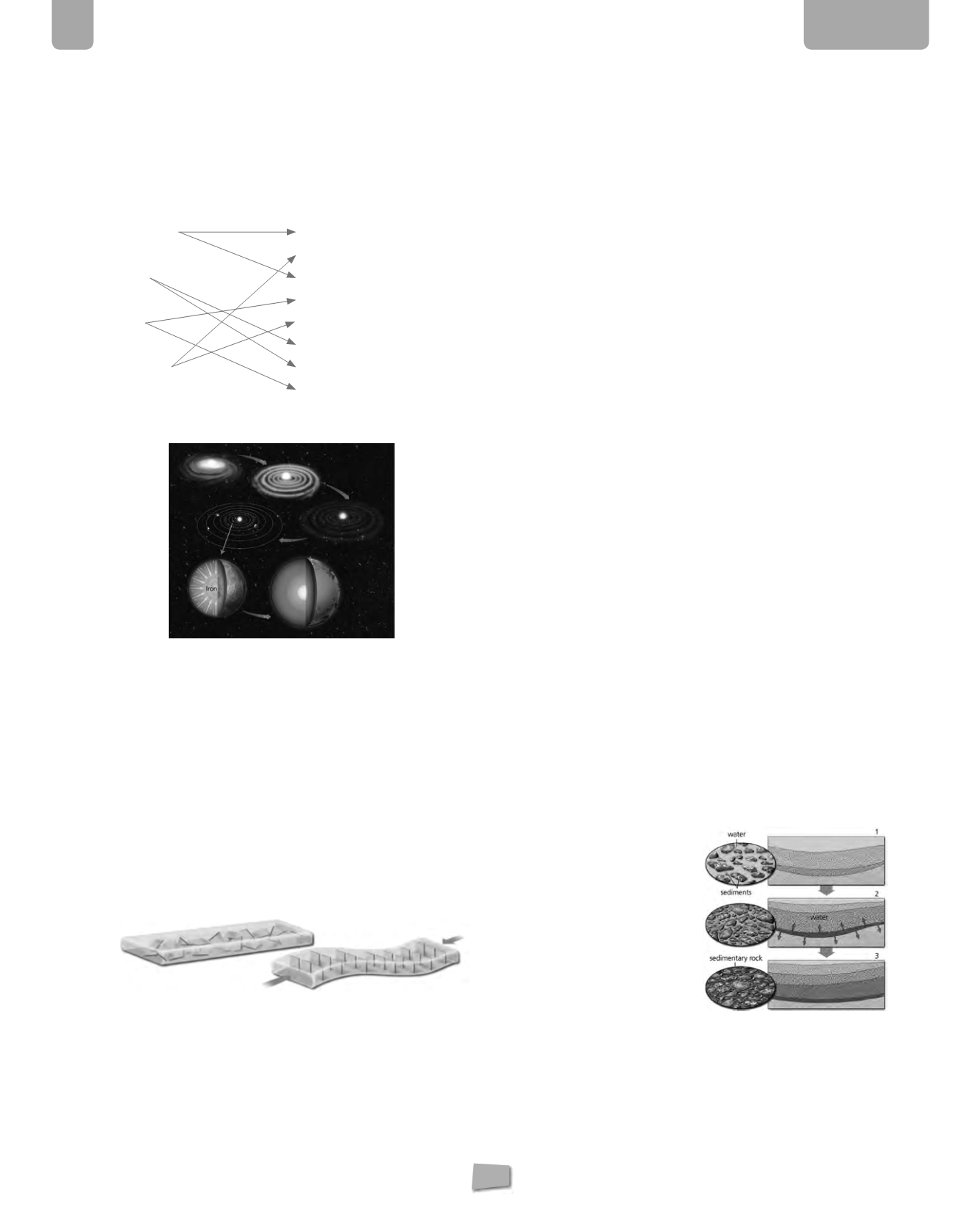
3.
Observe the following drawing and explain how the
Earth was formed.
4600 billions of years ago the Sun was formed from chemical
reactions in a giant cloud of dust and gas called nebula. In the
cloud of matter that surrounded the Sun, smaller dust particles
collided and grew in size. This process which formed the
planets is called accretion of planetesimals.
For 1000 million years the Earth was incredible hot. Due to the
immense heat stored in the Earth’s interior, there was a lot of
volcanic activity during the period. As the Earth’s temperature
decreased, gravity pushed heavier elements, such as iron,
towards the Earth’s interior. Lighter elements, such as oxygen,
moved towards the Earth’s surface. This process is called density
differentiation.
4.
Draw an explanatory diagram of the parallel layers of
minerals in foliated metamorphic rocks. Why does this
reorientation happen?
It happens because of the pressure on the rocks.
5.
Correct the following statements.
a) Volcanic rocks cool slower than plutonic rocks.
Plutonic rocks cool slower than volcanic rocks.
b) Basalt is the most abundant volcanic rock in the
continental crust.
Granite is the most abundant volcanic rock in the continental crust.
c) Plutonic igneous rocks are also called extrusive rocks.
Plutonic igneous rocks are also called intrusive rocks.
d) Granite is the most abundant volcanic rock in the
continental crust.
Granite is a plutonic rock.
6.
Answer the following questions:
a) What is the effervescence of a mineral?
It is the capacity to produce bubbles in contact with acids.
b) What does it mean if a mineral has a crystalline
structure?
It means that the particles are arranged to form a geometric
structure that is repeated constantly.
7.
Indicate the ore that correspond to each mineral.
a) Bauxite:
aluminium
b) Chalcopyrite:
tin
c) Galena:
lead
d) Hematite:
iron
8.
What are decorative rocks and what are they used for?
Give some examples.
Decorative rocks are the ones that after cut and polished
are so beautiful that they could be used to make sculptures,
building floors or any other element of decoration. Marble,
granite and basalt are great examples of decorative rocks.
9.
Explain the rock cycle.
The rock cycle is a series of processes that a rock goes through
to transform into another type of rock. These processes occur
very slowly, so the rock cycle takes place over millions of
years. All rocks, exposed to the action of wind and water,
can undergo the processes of erosion, transportation and
sedimentation. Sediments deposited in sedimentary basins
undergo the process of diagenesis or lithification and are
transformed into sedimentary rocks.
The rocks in the Earth’s crust are subjected to high pressures
and/or temperatures from metamorphic rocks. If the mineral
melts, magma will form. Magma can rise and cool under the
crust, creating plutonic igneous rocks. Magma can also come
out of the crust to the exterior and solidify, creating volcanic
igneous rocks.
10.
Look at the following
diagram and explain
the format ion of
sedimentary rocks.
The process in which
sediments transform into
sedimentary rocks is called
diagenesis or lithification.
Sediments deposited in
sedimentary basins (1)
often follow two essential
processes for the formation of sedimentary rocks:
Compaction (2) is when sediments lose volume. Due to the
weight of the sediments on top, water is lost and the sediments
become compacted.
Cementation (3) takes place after the water is lost and the
salts form crystals. The crystals act like cement and stick the
sediments together to form sedimentary rocks.


