50
2.1.2.
Mechanical properties
❚
Hardness
describes a mineral’s
resistance to scratching. To check if
a mineral is harder than another, we
can scratch one with the other. The
mineral that is scratched is softer than
the mineral that scratches it.
We can use minerals that are listed on
the
Mohs scale
to identify hardness.
This scale grades the hardness of 10
minerals from 1 to 10. The softest
mineral, talc (1) can be scratched by
all the others. At the other end of the
scale, diamond (10) can scratch all
the other minerals and can only be
scratched by another diamond.
❚
Cleavage
describes the way a mineral breaks. Many minerals break to show flat
surfaces, maintaining the crystalline structure. For example, galena breaks into
cubic shapes and gypsum breaks into sheets.
❚
Tenacity
describes how easily a mineral breaks. A fragile mineral breaks easily,
such as talc.
Some minerals can be pulled into thin threads. This is the case of copper threads
that conduct electricity. This is called
ductile
tenacity.
2.1.3.
Magnetic properties
Some minerals, such as
magnetite
, behave like a magnet. They attract objects
that contain iron and nickel.
2.1.4.
Other properties of materials
❚
Transparency
describes how a mineral reacts to light. A mineral can be
transparent
, such as diamond, when light can pass through it;
translucent
,
like quartz, when light passes through it but is distorted; or
opaque
, like
galena, when no light can pass through.
❚
Density
is the relation between the mass and volume of a mineral (density
= mass/volume). Density is usually measured in grams per cubic centimetre
(g/cm
3
). This property is specific to each mineral and is independent of size.
So, the density of a mineral is important information for identifying minerals.
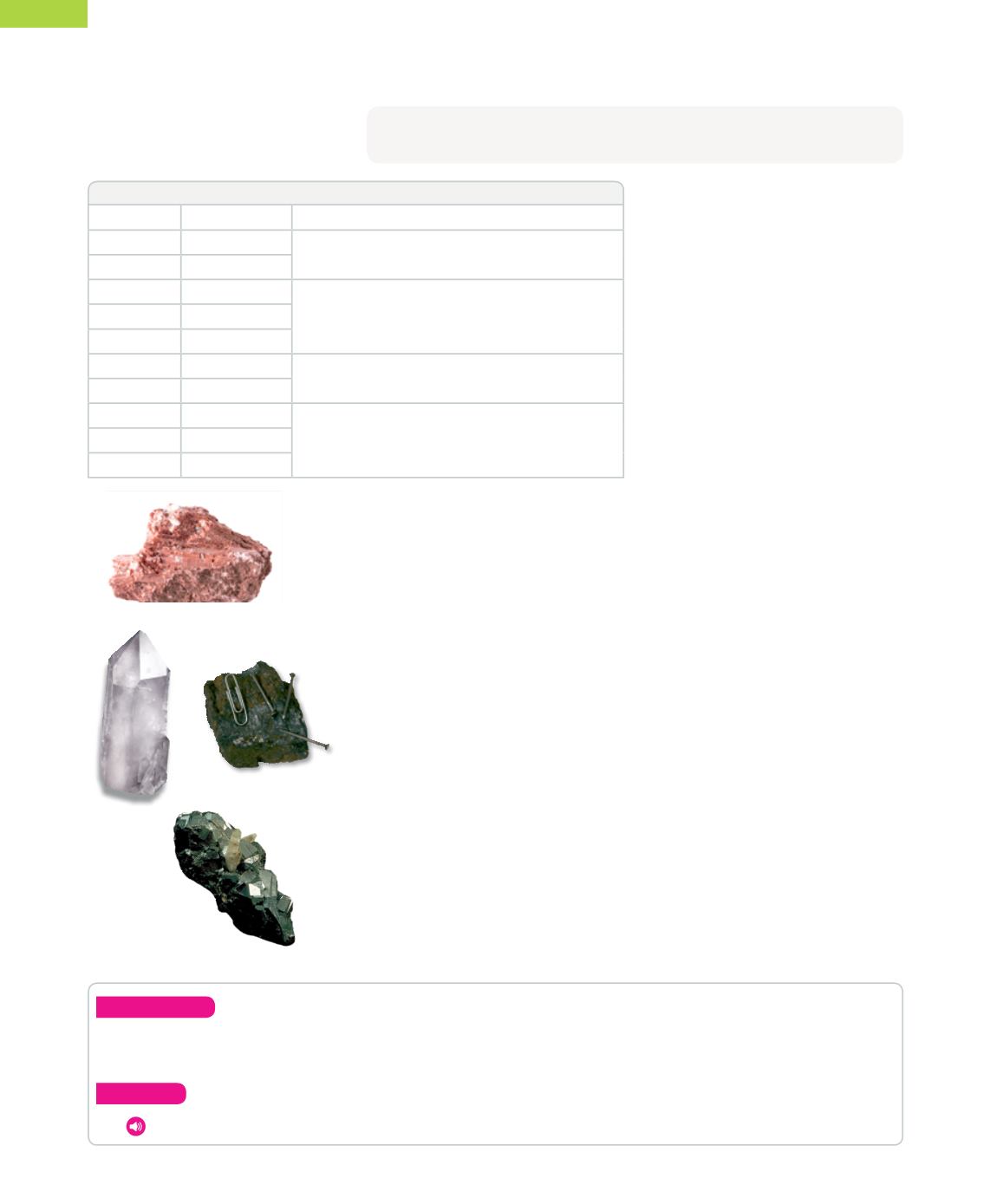
Gypsum
Magnetite
Mohs scale
Hardness
Mineral
Characteristics
1
Talc
Very soft, because it can be scratched by another
mineral.
2
Gypsum
3
Calcite
Soft minerals that can be scratched by the point of
a knife.
4
Fluorite
5
Apatite
6
Orthoclase Hard minerals. Orthoclase can be scratched with
sandpaper and quartz scratches glass.
7
Quartz
8
Topaz
Very hard, cannot be scratched by any other
mineral.
9
Corundum
10
Diamond
Galena
Quartz
The
mechanical properties
of minerals refer to how the mineral behaves
when a force is applied to its surface.
Understand
12.
Explain in your own words what the Mohs scale is? What is it used for?
13.
A crystal is hit and breaks into small cubes. What property does this describe?
Analyse
14.
Listen and say which mineral properties are being described.


