53
3. The geosphere
www
3.1.
Igneous rocks
In some areas of the upper mantle, minerals melt due to high temperatures.
When magma rises to the surface it can remain in the crust or it can exit to the
exterior. In both cases, away from the source of heat, magma cools until it becomes
solid and forms
igneous rocks
or
magmatic rocks
.
These rocks are made up of one or several minerals compressed together, so they
are extremely compact. The resistance of igneous rocks to pressure makes them a
perfect material to construct buildings.
Igneous rocks are classified as volcanic or plutonic depending on where they were
formed.
❚
Volcanic igneous rocks
or
extrusive
rocks are formed when magma rises and
leaves the Earth’s crust as lava. Lava cools quickly and forms volcanic rocks.
❚
Plutonic igneous rocks
or
intrusive rocks
are formed when rising magma
cools slowly inside the Earth’s crust. The mineral crystals are easily visible as they
had more time to form.
Magma
is a substance made up of melted materials mixed with gases and
water, formed in the Earth’s interior.
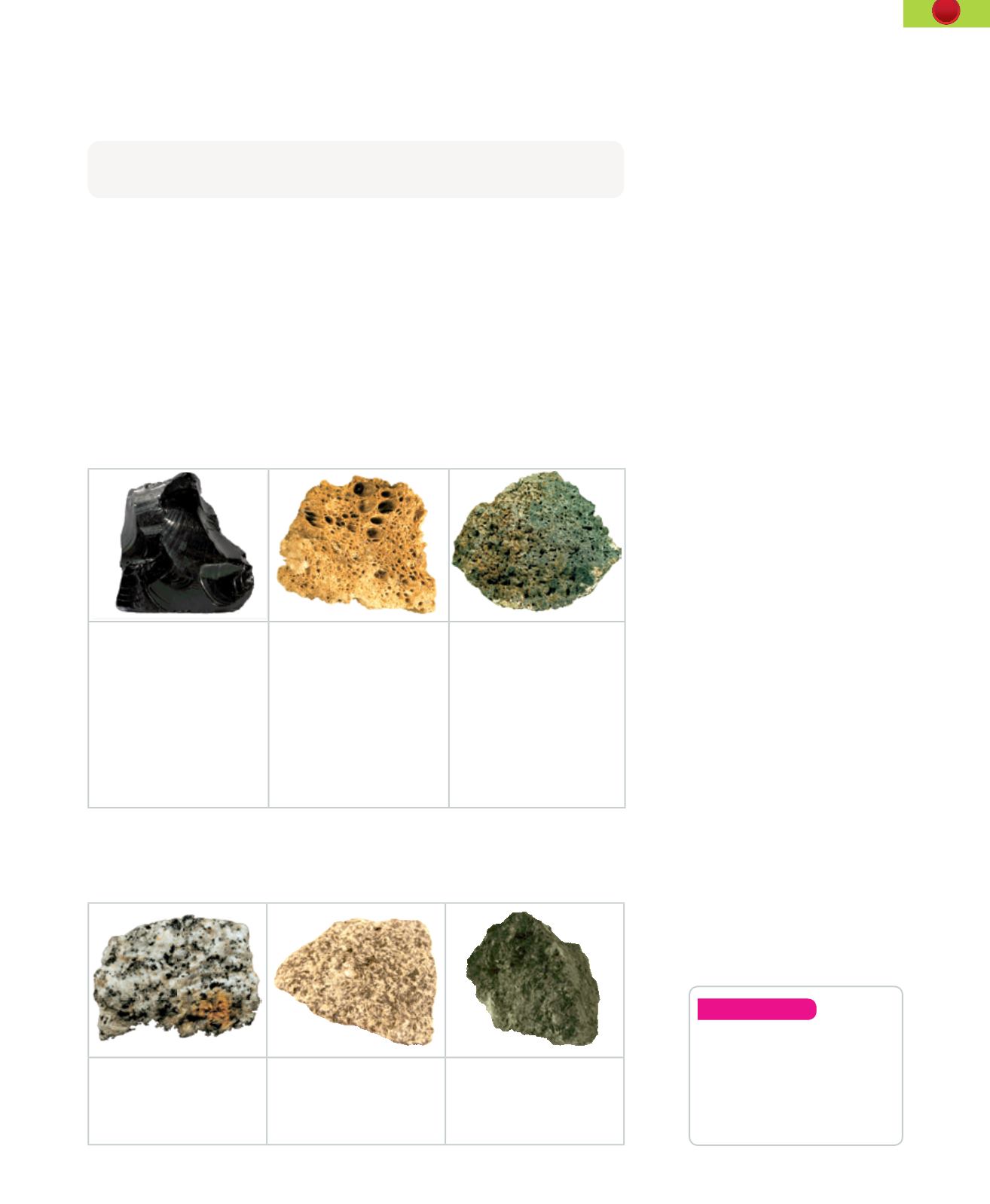
Obsidian
is shiny black
and originates in the
continental crust. It has a
glassy texture. The crystals
have not had time to
form.
Pumice
or
pumice stone
is a continental rock. It is
easily recognised because
of the many small holes
in the surface. These were
formed by gases that
were in the rock before it
solidified.
Basalt
originates in
submarine volcanoes.
It contains very small
minerals due to its rapid
cooling. It is the most
abundant rock found in
the Canary Islands and
the ocean floor.
Granite
is the most
abundant plutonic rock on
the continental crust.
Syenite
is a continental
plutonic rock.
Gabbro
is a plutonic
rock found in the oceanic
crust.
Understand
20.
Explain why crystals in
the minerals that make
up plutonic rocks are
visible, but are not visible
in theminerals of volcanic
rocks.


