5
Structures
112
4.5.
Reinforced concrete structures
The importance of framework structures lies in the fact that
they are mostly used in the construction of buildings and
houses.
It makes no difference what material they have been built from
because they all function in a similar way and the result is the
same. They both pass on the load from a particular place to
the foundations, creating living space between the floors of
the building.
If you know about a building under construction near the
school, you can organise a short visit or, for homework, get the
students to find out about the type of concrete slab which is
being used (one-directional blost with bricks, bidirectional with
panels, flat slabs …) and how it is being built. To do this, you
can ask students to take photos of the construction work and
use them to point out the features which they have learned
about.
In order to support the explanation it is a good idea to point
out structural elements in the classroom which are mentioned
in the text.
4.6.
Laminated structures
Laminated structures provide considerable resistance despite their
limited thickness because their particular curved shapes make
them behave like vaults or cable cars.
The easiest way to explain this is by getting students to think of
the piece of metal used to cover holes in the road. It is not very
thick, but can bear the weight of vehicles because it bends when
they pass over it, changing itself into an inverted arch that can
withstand traction instead of bending.
4.7.
Pneumatic structures
Structures of this type are not rigid and are of limited use.
They are basically used to cover spaces, but it is not possible to use
them to construct buildings that bear weight.
4.8.
Spatial and geodesic structures
In this section we look at spatial grid structures.
They are structures which combine the advantages of triangular
structures with those of domes and three-dimensional structures.
Their advantage is that they only require two types of parts for
their construction (linear bars and nodes), which is why they are
very quick to assemble.
Animation:
TYPES OF STRUCTURES
Animation in the form of an activity. This involves matching each
photo of a structure with the type of structure.
Answer key
Apply
18.
Listen and point to the different elements in the
structure of this building. Then trace the route of our
weight until it goes down to the ground.
In the photo we can see the deck’s side beams and the pillars
of two of the floors. The loads placed on the framework
are first passed on to the joists. These pass them on to the
main beams and from there they go down from one floor to
another until they reach the foundations of the building.
108
109
5. Structures
5
+
www
4.5.
Reinforced concrete structures
Concrete
led to major
advances
18
in construction because it could be made into
any shape. Concrete resists compression and with steel
rebar
19
frameworks it can
also bear traction.
It isaverystrongmaterialwhich isused inall typesofbuilding,mostly in framework
structures like your school:
❚
Under the floor you are on
there is a horizontal structure
called
slabs
, which consist
of small beams called
joists
and material in between them
(ceramic blocks, bricks or
polystyrene).
❚
The slabs transfer your weight
to the
beams
(made of
concrete and steel rebar) and
then to the
columns
(vertical
supports).
❚
Thecolumnsdon’t sitdirectlyon thegroundbecause theywould sink.Between
the columns and the ground are the
foundations
, which spreads out the
weight of the building and its load.
❚
Reinforced concrete can be used to build huge arches, bridge piers, plates and
roofs, as well as pillars and beams in structures.
4.6.
Laminated structures
Theseareformedby laminatesofmetal,plasticorcompositematerial likereinforced
concrete. Their
curved shape
and
folds
give them their strength.
❚
The curved shape makes the laminates bear the stress of traction and
compression on their surface.
❚
The folds and
ribs
20
give rigidity in exact points. So, for example, the rim on a
plastic cup prevents the cup from deforming when we drink and the grooves
on the side make it stronger when we hold it.
4.7.
Pneumatic structures
Pneumatic
structures are
light
and easy to transport,
set up
21
and
dismantle
22
.
Forthisreason,weusethem inconstructions likefieldhospitalsorfunfairattractions
for children. These structures use compressed air inside them. When they expand,
they stretch the outer plastic surface. This makes them stay
upright
23
.
4.8.
Spatial and geodesic
These are three-dimensional structures of bars, which combine the properties of
vaults with triangulated structures to create curved shapes and cover large spaces.
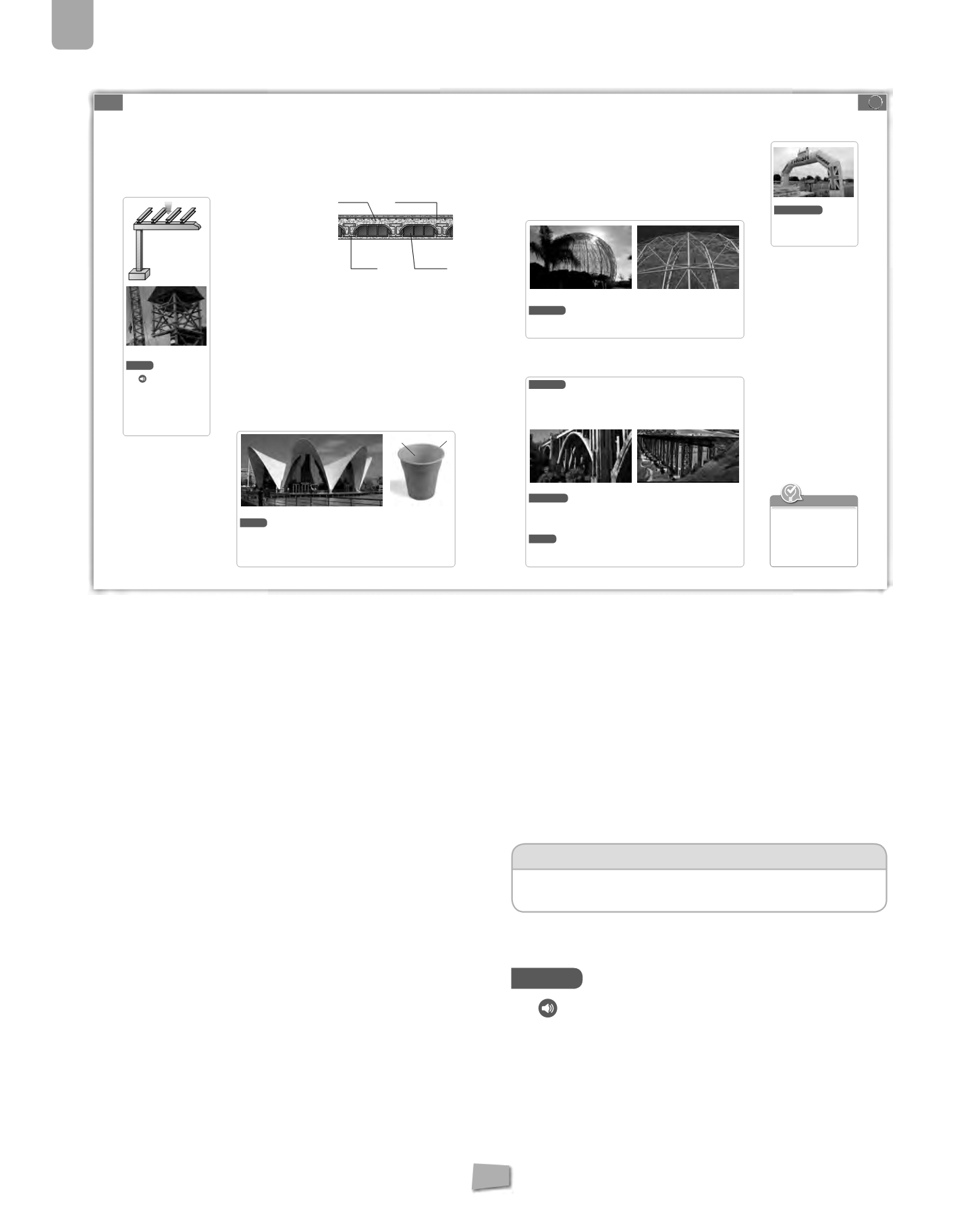
Sectionof slab
.Observehow thebricks areplaced
between the joists.
steelmesh (rebar)
concrete
joist
ceramicblock
Apply
19.
Experiment with laminated structures. Place a sheet of paper flat
between two desks. Does it stay horizontal? Try again, but this time,
bend the sheet of paper like the structure in the photo. What happens?
Why?
Analyse
21.
Look at the photo. How do the bars join the metal nodes? What kinds
of stress are acting on these nodes?
The
Oceanográfico
by FélixCandela
Geodesicdomeof the
Oceanográfic
in the
SciencePark inValencia
The viaduct inMadrid
Detailof thenode
24
of thegeodesic
structure
TheHacha viaduct,Granada
Understand
20.
Look at the photo. Can
this type of structure
support bending?
Analyse
22.
Many structurescombine severalof theoneswehave seen.Examine the
viaducts in the photos and say what structure types and materials are
used in them. Can you find the relationship between the shape and the
material of the parts and the types of stress they bear?
Evaluate
23.
Think about the materials that you could use for your bridge: thread,
paperbars,wire, cardboard,balsawood,etc.Howandwhywillyouuse
these materials for building the different parts of the model?
Apply
24.
Thinkabout thedifferent structure typeswehave lookedat.Whatkind
of bridge do you want to build for the unit project? Draw a sketch.
❚
Artificialstructuresaremade
by humans.
❚
Structures can be: massive
or lintels, vaulted, triangular,
suspended,reinforcedconcrete,
laminated,pneumatic,spatial
and geodesic.
Key concepts
They consist of linear bars and nodes that connect them. They use triangles
and tetrahedrons, the three-dimensional equivalent of triangles, because these
shapes cannot be easily deformed.
weight
beam
column/pillar
foundations
joist
Abuilding structure
Apply
18.
Listen and point to
the different elements
in the structure of this
building. Then trace
the route of our weight
until itgoesdown to the
ground.
18
advances
:
improvement or progress
19
rebar
: strong steel bars used in
construction
20
ribs
:
like thebones in your chest
21
setup
:
to put together, construct
22
dismantle
: take apart, intopieces
23
upright
: standing, vertical
24
node
: a point in a framework where
lines or bars join or intersect
rim
grooves


