22
1. Prehistory: the Paleolithic age
36.
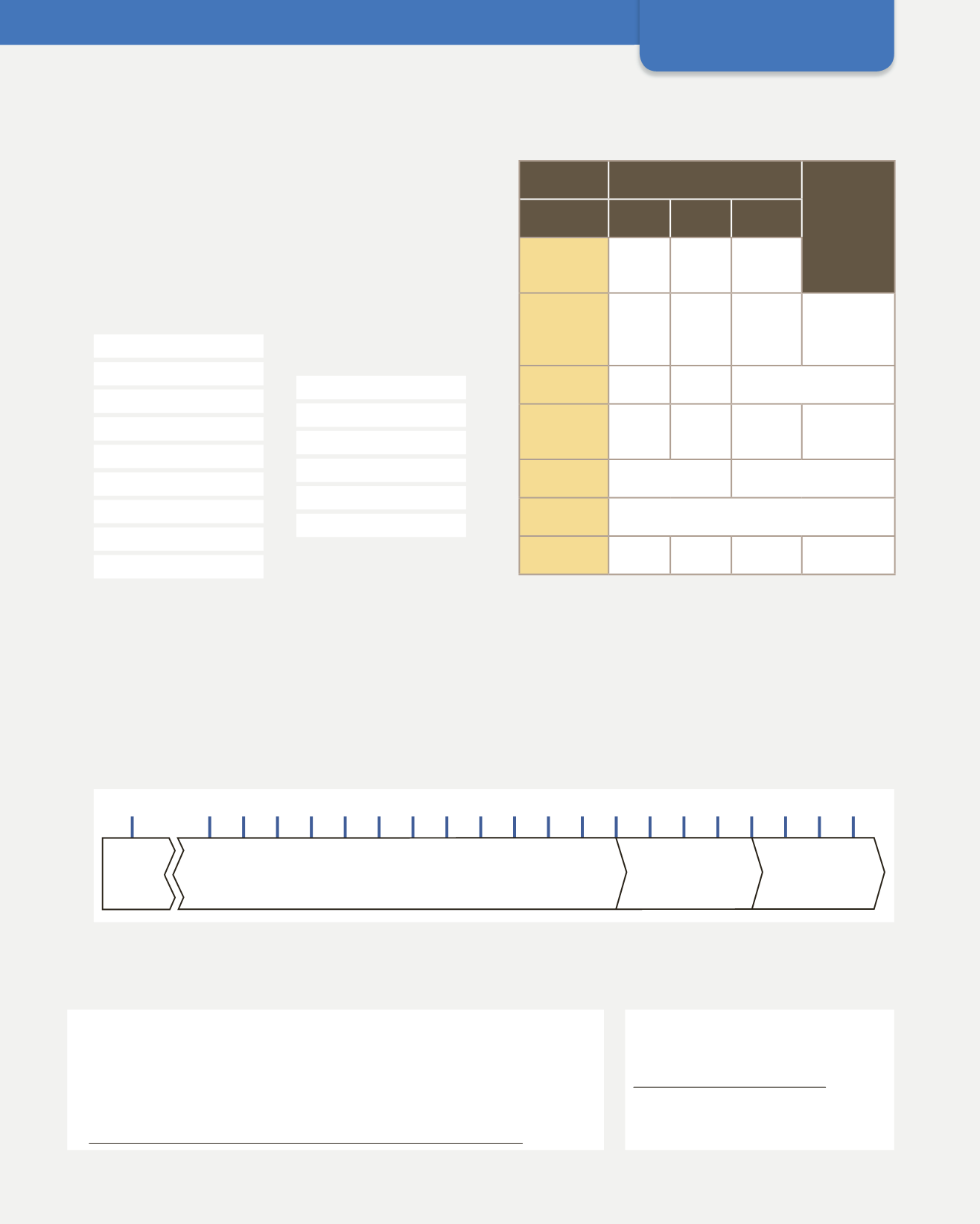
Copy this table into your notebook and complete it
with the corresponding information.
Paleolithic
Epipaleolithic
Lower
Middle
Upper
Chronology
(world)
Chronology
(Iberian
Peninsula)
Hominids
Tools and
technology
Economy
Society
Culture and art
Period
34.
Copy the timeline below in your notebook and follow the instructions.
a) Colour in the following periods of Prehistory on the timeline: Upper Paleolithic, Neolithic Period, Bronze and Iron Ages.
b) Mark the exact time the following discoveries took place with an arrow:
❚
The appearance of writing (3500 B.C.)
❚
The appearance of agriculture and livestock farming (8000 B.C.)
❚
The approximate date of the Altamira cave paintings (15000 B.C.)
❚
The beginning of copper metallurgy (4000 B.C.)
32.
Define the following terms in your notebook.
Bronze and Iron Ages
Upper Paleolithic
Neolithic
Epipaleolithic
Middle Paleolithic
Lower Paleolithic
Venus
knapped stone
bow
biface
harpoon
copper
Levantine painting
Neanderthal
bronze sword
❚
site
❚
Prehistory
❚
Paleolithic Period
❚
predator
❚
glacial period
❚
hominisation
❚
tribe
❚
engraving
❚
polychrome
❚
schematic
33.
Match the terms on the left with the correct period
on the right in your notebook.
35.
Match the causes in the left column with the consequences on the right and make sentences about the hominids
in your notebook. For example:
Improvements in their diet led to an increase in the population and consequently
they extended their territory.
CAUSES
❚
One of the anatomical changes was the development of opposable thumbs…
❚
They held religious beliefs and practised magic rituals…
❚
Through observing nature, they discovered fire…
❚
Improvements in their diet led to an increase in the population…
10000 B.C.
5000 B.C.
40000 B.C. 20000 B.C.
1000 B.C.
CONSEQUENCES
they improved their diet.
they extended their territory.
they did cave paintings.
made manual work easier.
1
CONSOLIDATION


