2
28
2. The Neolithic period and the Bronze and Iron Ages
1. THE NEOLITHIC PERIOD
When the last glacial period ended around 8000 B.C., there was an increase in the
Earth’s temperature. The flora and fauna changed, and human beings had to adapt
to these new conditions. They learned to
cultivate the land (agriculture)
and
domesticate animals (livestock)
. These innovations marked the beginning of a new
historical period called the
Neolithic Period
.
These discoveries were made by
observing nature
. People observed how wild seeds
that fell on the ground grew into plants. They began to sow
1
wheat
and
barley
.
Eventually, the best seeds were selected and
more abundant harvests
were obtained.
At the same time, they discovered that they could domesticate animals and breed
them in captivity. This was easier than hunting and guaranteed a steady supply of
meat
,
milk
,
leather
and
wool
.
In the Neolithic Period, new tools made from polished stone were created for the new
activities.
These changes occurred in several places at once. One of the earliest Neolithic
settlements was in the
Fertile Crescent
in the
Near East
. Neolithic culture spread all
over the world from these points. Meanwhile, Neolithic and Paleolithic tribes coexisted.
The changes were so dramatic that it is called the
Neolithic Revolution
.
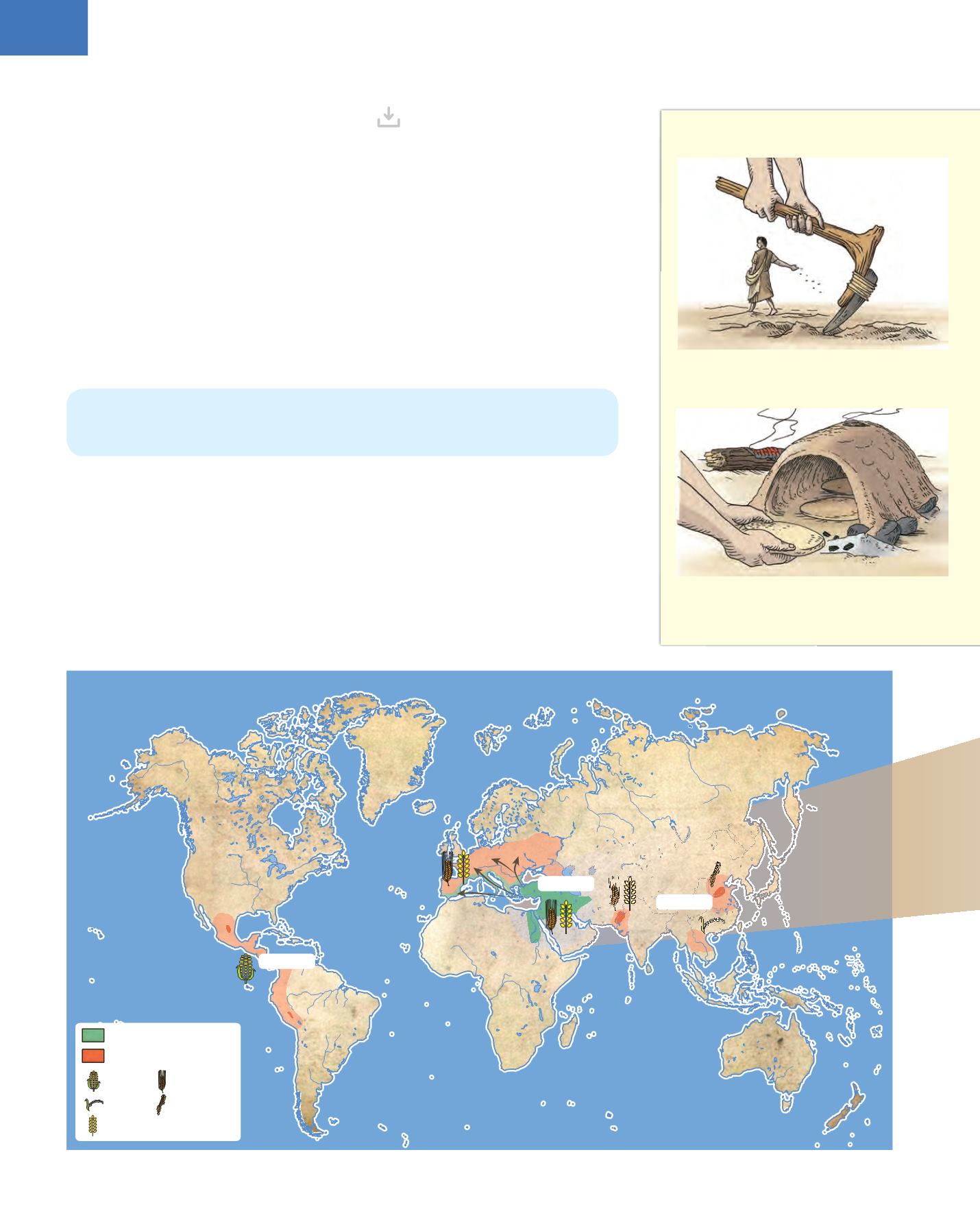
Tilling and sowing
: the land was turned
over and sown with hoes and ploughs.
Fertile Crescent
other Neolithic Settlements
corn
rice
wheat
barley
millet
I N D I A N
O C E A N
P A C I F I C
O C E A N
AT L A N T I C
O C E A N
P A C I F I C
O C E A N
8000 B.C.
7000 B.C.
3500 B.C.
Baking bread
: bread was made by mixing
flour with water and heating it in an oven.
In the Neolithic Period, the way of life of human beings changed completely. They
changed from
predators
to
food producers
. As they were able to feed a larger
number of people, the
population
increased.


