➁
➂
➃
➄
2
2. Relief
37
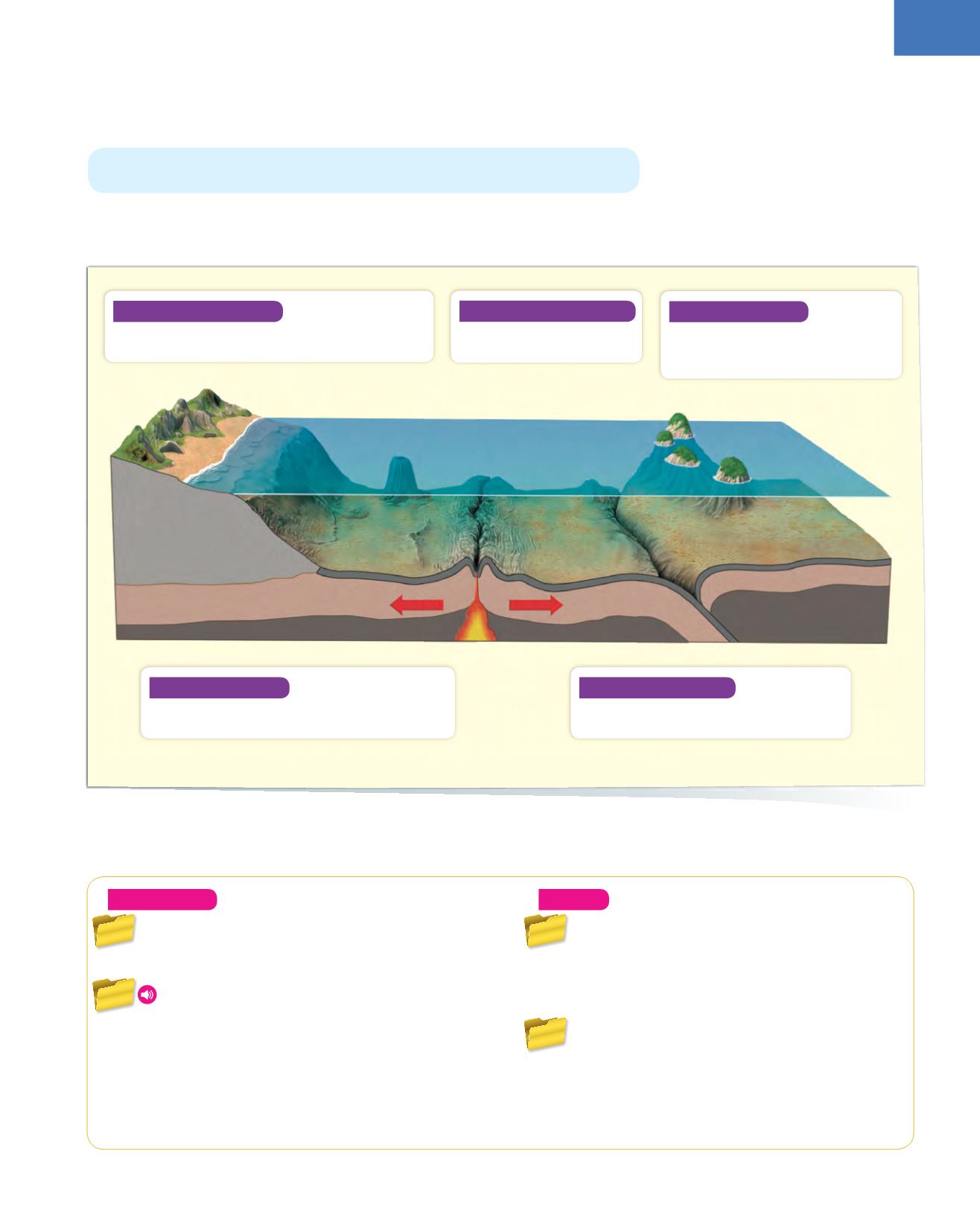
4.3. The relief of the ocean floor
There are two main areas of submarine relief: the
continental shelf
and the
ocean floor
.
Most of the
landforms
on the
Earth’s crust
are under the
seas
and
oceans
. These
landforms make up the
submarine relief
.
Continental shelf
➀
An extension of the
continent below the water. It runs along the coast
and is relatively shallow (up to 200 m).
Ocean ridges
➃
Mountains or mountain
ranges, usually of volcanic origin, formed in the
areas of contact or separation of tectonic plates.
Abyssal plain
➂
An enormous
area of the ocean floor that is
relatively flat and is as deep as 4 000
m in some parts.
Continental slope
➁
A sharp descent at the end
of the continental shelf.
Ocean trenches
➄
Deep depressions
(reaching depths of over 10 000 m) that
originate in areas where tectonic plates meet.
➀
Understand
15.
Classify these landforms into horizontal or with steep
slopes: hill, plain, plateau, mountain range, valley,
mountain.
16.
Listen and say the coastal landform. In your
notebook, explain the difference between a cape and
a gulf, a cliff and a beach, and a delta and an estuary.
17.
Compare continental relief and submarine relief.
Discuss the similarities and differences.
18.
Which agents that shape relief don’t affect submarine
relief?
Create
19.
Look at a
physical map of your autonomous
community
. Locate some landforms near
where you live. Compare the local relief with
the relief of the rest of your autonomous
community.
20.
Locate examples of the following landforms on
a
physical map of the world
: a cape in Africa,
an archipelago in Asia, a peninsula in Europe,
and an island in Oceania. Present the examples
you have found to the class and describe the
geographical location and their characteristics.


