27
2. The Earth in the Universe
www
1.4.
Composition of the universe: galaxies
Because the Universe is immense, we only know a very small part of it, in which there
are countless galaxies.
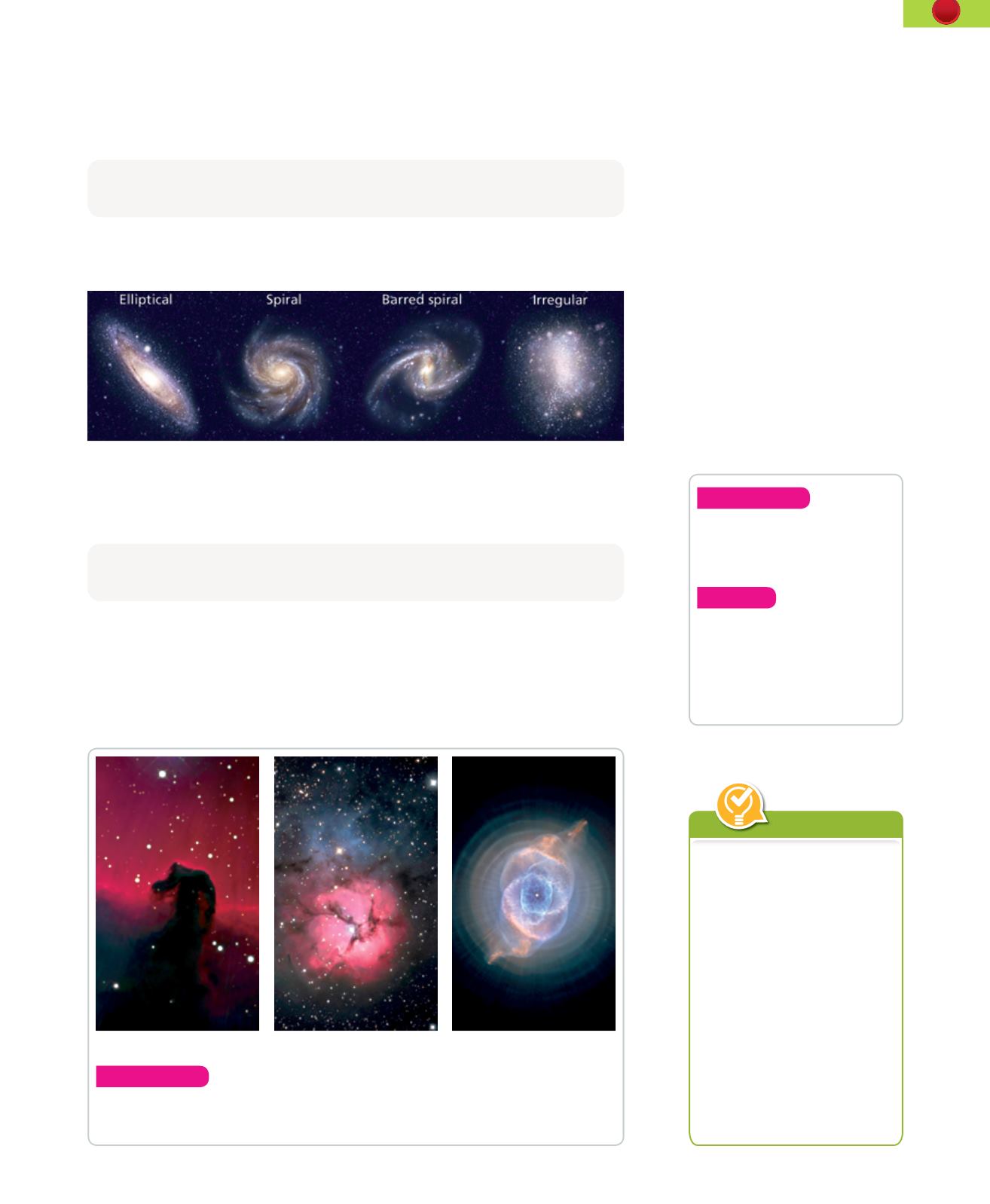
Galaxies can have different shapes: elliptical, lenticular, spiral, barred spiral, and
irregular. Spiral galaxies are the most common.
Galaxies group together forming
clusters
. These clusters can be composed of
hundreds or even thousands of galaxies.
1.4.1.
Nebulae
Although they do not contain stars, nebulae could have been formed from the
remains of old stars that exploded.
Some nebulae are places where stars are formed. These are born from the
concentration of gases and an increase in temperature. This is why nebulae and
clusters of stars are frequently found together.
Galaxies
are huge group of stars, nebulae and interstellar dust and gas held
together by the force of gravity
1
.
Nebulae
are huge clouds of gas. They are formed by concentrations of
hydrogen and helium as well as interstellar dust.
Horsehead
Trifid
Cat’s eye
Remember
9.
Find out what causes the colour of the nebulae you can see in the photos.
Write a short report.
Remember
7.
Discuss the differences
between a galaxy and a
nebula.
Create
8.
Find out the names of
the nearest galaxies to
us. Describe their shape
and write their distances
from our galaxy.
7
Key concepts
❚
The universe is all the space,
matter and energy that exists.
❚
The Big Bang theory is the
most widely accepted theory
to explain the origin of the
universe. The theory of inflation
explains the first moments
after the Big Bang.
❚
To measure the distances
between galaxies, we use a
light year, a parsec and an
astronomical unit.
❚
A galaxy is a group of stars,
nebulae and interstellar dust
and gas.
1
gravity
:
attraction of bodies
according to their mass


