5
Structures
134
1.
Define in your own words the following structural
elements. Draw a picture where necessary.
Element
Definition
Block
Domed element of the slabs which
reduces the weight of the slab by filling in
the spaces between joists.
Cable suspender
Linear element normally made of steel,
and which bears traction forces.
Pile
Underground pillar or column which can
be driven to a sufficient depth so that it
rests on firmer soil.
Cross-bracing
Element that gives rigidity by using
triangular structures.
Lintel
Horizontal element that spans a door or
window space. It bears bending forces.
2.
Indicate whether the following statements are true or
false, and why.
a)
Cable suspenders use compression because that way
they never break.
False.
Cable suspenders only offer resistance to traction.
This is their only way of working..
b)
A pile is a big-sized pillar.
False.
A pile is a foundation system that involves driving
underground pillars (of the necessary size) in order to rest
on firmer soil.
c)
Massive structures are made of metal.
False.
Solid structures are made of stone; metals are used in
the form of bars to construct light structures.
d)
Triangular structures can be made out of many
materials.
True.
They can be made of wood, steel or aluminium.
e)
Materials are much more important than the shape
when it comes to the resistance of structures.
False.
Both are equally important, as a good design saves
on materials.
3.
Draw an arch, label its parts and explain why it was a
structural advance.
Arches represented a great structural advance. They made it
possible to span spaces by bearing compression forces, and led
to an increase in the size of the distances covered. Compression
forces are the ones most suited to stone – a material that has
been used since antiquity in building.
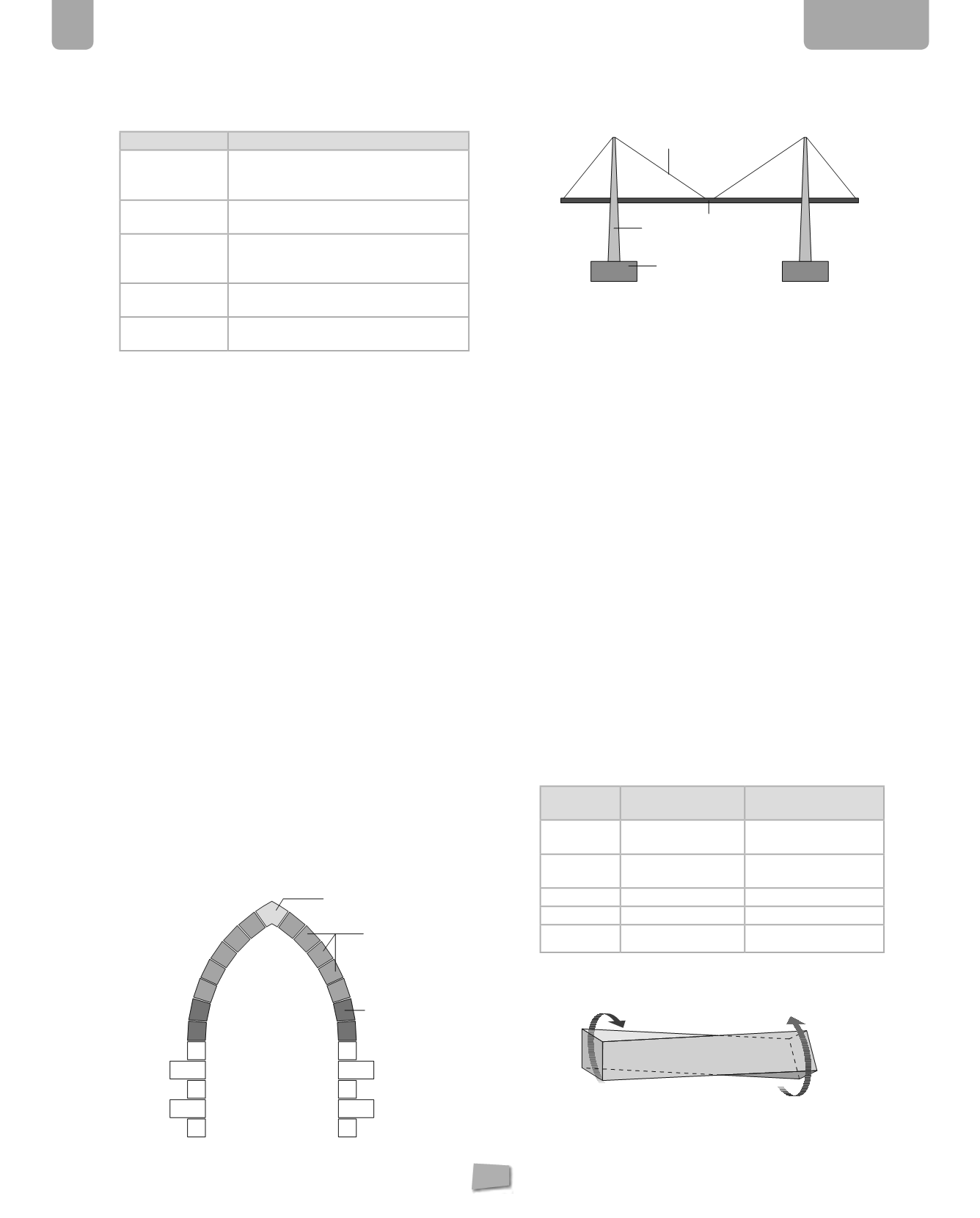
4.
Name the different elements of this bridge, and say
what stress is acting on each.
a. deck: bending
b.cable suspenders: traction
c. pillar: compression
d.plinth: compression
5.
Explain the differences between stability, resistance and
rigidity.
Stability is the property of bodies that are difficult to move;
resistance is associated with the capacity to bear stresses
without breaking apart; rigidity is the capacity of the body to
not lose its original shape under the action of these stresses.
6.
Name the parts of a framed structure and explain the
shape and function of each.
Concrete slab
:
this is made of joists and blocks. It is on the
surface that separates each floor of a building. It is rigid and
continuous, and transfers loads to the beams.
Beams
:
the concrete slab rests on these. They are horizontal
elements made of metal or concrete that bear bending forces,
and sit directly on pillars.
Pillars
:
these are vertical elements that transfer the loads to
the ground from floor to floor. They rest on the foundations.
Foundations
:
these form an intermediary level between
the pillars and the ground, and increase the surface of the
building’s support base.
7.
Specify what type of structure the following buildings
are, and number them in order of their age.
Order
of age
Building
Structural type
4
The Eiffel Tower
Structure with
triangular metal bars
2
The Segovia
Aqueduct
Structure with arches
5
your school
Framed structure
1
The Keops Pyramid
Solid structure
3
Burgos Cathedral
Domed structure
8.
Draw arrows on the bars to show the various forces that
can affect them. Give an example of each.
Torsion
: Axle of a car when it is starting up; the shaft of a
screwdriver when it is tightening a screw
riñones
clave
dovelas
a
b
c
d
EXAM B


