124
Structures
5
Answer key
48.
List five loads that can act on your body. Say which
ones are fixed and which are variable.
Student’s own answer. My own weight: fixed; a shopping bag:
variable; a rucksack: variable; the wind: variable; a child pulling
you by the hand: variable.
49.
Name the most common types of stress. Explain when
each thing happens and give an example.
Traction: when forces try to pull the body; a catapult.
Compression: when forces try to compress / squash the body;
the foot of a standard lamp.
Bending: when forces try to bend the body; a bookshelf
containing a lot of books.
Torsion: when forces try to twist a body: an axis at the start of
its turn.
Cutting: when forces try to cut a body: a pair of scissors.
50.
Listen to the following statements. Are they true
or false? Give reasons for your answers.
1.
The cutting force is only exerted when something is
cut.
False, the same force is exerted whether the paper is cut
or not.
2.
Traction is a force that generally pulls an object.
True. Traction occurs in a body when the forces acting on
it travel in the same direction or opposite directions.
3.
A human skeleton is subjected mainly to the force
of compression.
True. This affects mainly the spine and the bones in the feet.
4.
A plastic glass has no type of structure.
FFalse. The glass is a structure in its entirety.
51.
Analyse what types of stresses act on the following
natural structures: a bird’s nest, an elephant’s foot,
the wings of a bat while flying and a termite’s nest.
❚
Bird’s nest: traction
❚
Bat’s wings: bending
❚
Termite’s nest: compression
❚
Elephant’s foot: compression
52.
Draw the following structures and describe the
stresses acting on each of their parts:
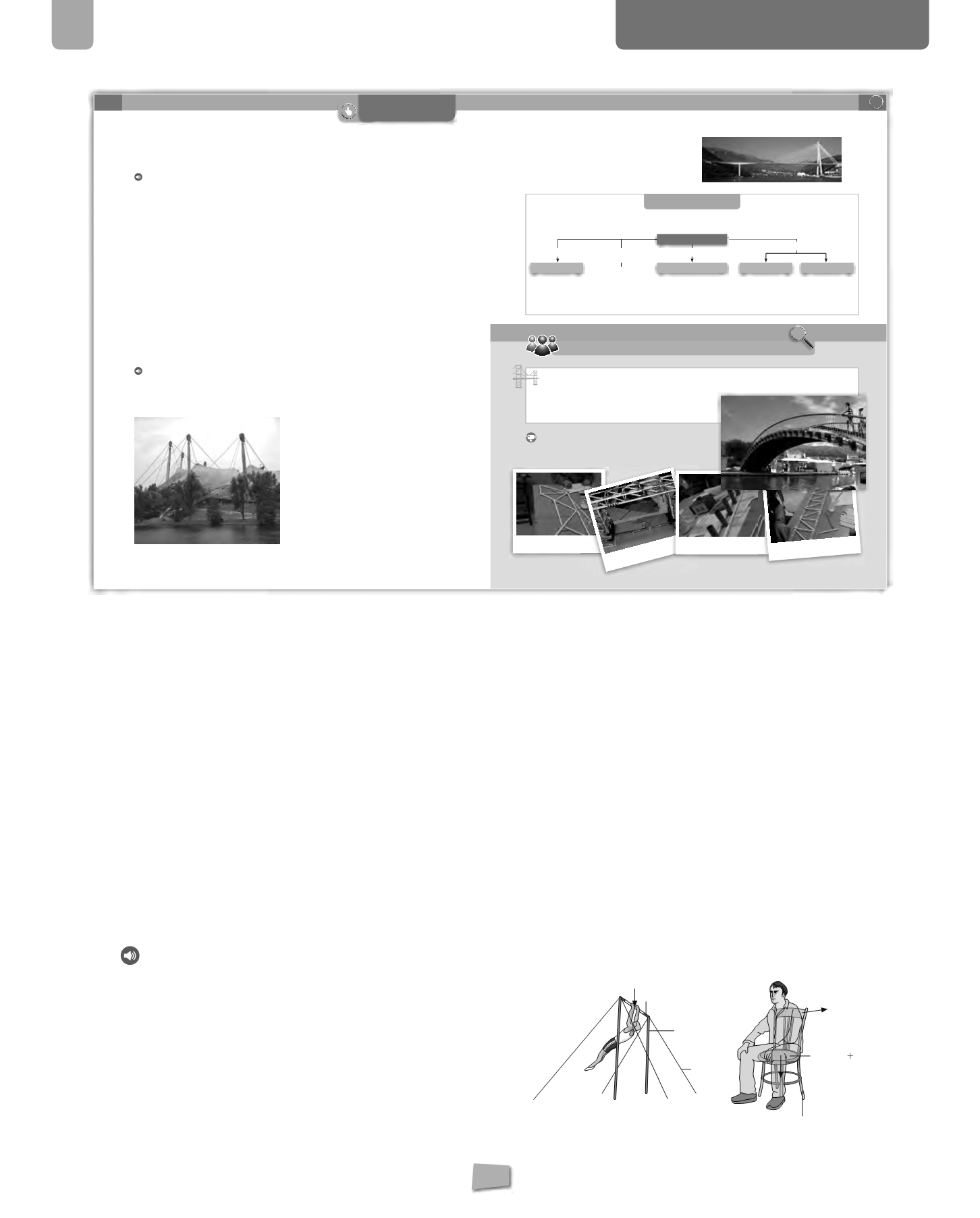
a)
A bar used for exercises in gymnastics.
b)
A swing.
c)
A chair.
d)
A ceiling fan.
compression
bending
compression
bending
bending
compression
traction
124
5
+
www
48.
List five loads that can act on your body. Say which
are fixed and which are variable.
49.
Name the most common types of stress. Explain
when each thing happens and give an example.
50.
Listen to the following statements.
Are they true (T) or false (F)? Give reasons for your
answers.
1 _____ 2 _____ 3 _____ 4 _____
51.
Analyse what types of stress act on these natural
structures: a bird’s nest, an elephant’s foot, the
wings of a bat while flying and a termite’s nest.
Draw some of them and indicate the stress with
arrows.
52.
Draw the following structures and describe the
stresses acting on each of their parts:
a)
A bar used for exercises in gymnastics
b)
A swing
c)
A chair
d)
A ceiling fan
53.
When we lean back in our chair, it is more likely to
break. Why is that? Give reasons for your answer.
54.
When we hang clothes on a washing line, what
stress does the line bear?
Think about your answer and keep in mind what
washing lines are made of.
55.
Listen and write the structural elements you
hear.
a)
Put them in the order that they were used in history.
b)
Look at the photo. Which elements appear?
c)
What type are they?
56.
What materials (wood, cement, stone or steel) are
used to make these structural elements: a beam,
suspenders, a plinth and a buttress?
Keep in mind that there might be other reasons to
use these elements, not just structural reasons.
57.
List the advantages of reinforced concrete over
stone.
58.
Answer the questions. Write a sentence in each
case.
a)
What is the difference between a beam and column?
b)
What is each one for?
c)
What are the foundations of a building for?
d)
When do you use shallow foundations and piles instead
of plinths? Why?
59.
Search the Internet for these famous bridges and
aqueducts.
Explain what type of structure each one is and
what materials they are made of:
❚
The Aqueduct in Segovia
❚
The Roman Bridge in Cordoba
❚
The Rande Bridge in Vigo
❚
The Barqueta Bridge in Seville
❚
The Viaduct in Madrid
❚
The San Pablo Bridge in Cuenca
60.
Read the following statements.Are they true (T)or
false (F)?
Give reasons for your answers.
a)
Triangular bar structures can be made of stone.
b)
Steel is used in solid structures.
c)
Suspenders are only used to make structures more
stable.
d)
Piles are thin columns used is small constructions.
61.
Cut out three rectangles of card 10 x 30 cm.
Fold them lengthwise and make three sections:
circular, triangular and square.
a)
If we put the same load on top of each section, for
example a pencil case, what type of stress are they
bearing? Does it have the same intensity in each
case?
b)
Despite being made of the same amount of material,
which one do you think will resist the stress better?
Why?
62.
Choose a piece of street furniture which is familiar
to you (a bench, a street light, a bin, etc.).
Analyse its form and structure.
Present your assignment with photos and
illustrations.
63.
Look at the bridge in the photo. It is made of two
very different structures. Identify them, name the
parts and say what type of stress each one bears.
Do you think the two parts of the bridge work the
same? Why?
As a final task in this unit, after you have finished building your bridge, write a report on a computer with the
following sections to go with your video:
1.
A general description of your bridge (the structure).
2.
The specifications (length, width, weight, height).
3.
The parts.
Building a bridge
CONSOLIDATION
Make a video of the bridge and test the resistance by adding
weight until it collapses.
This video will go with your written report.
STUDY TECHNIQUES
❚
Draw a mind map of the concepts in the unit. Use the following structure to get started:
❚
Write a summary using the key concept boxes in the unit. Include everything you think is important.
Structures
stress
man-made
natural
structural elements
They bear
Made up of
Functions
Distinctions
...
FINISHING THE FINAL TASK
+
www
125
5. Structures
CONSOLIDATION


