112
4.
TRANSFORMATION OF MOTION
Some mechanisms transform linear motion into rotary motion. Most of these
mechanisms are reversible. They also transform rotary motion into linear motion.
The linear motion can be unidirectional or reciprocating. Reciprocating motions
alternate from one side to the other.
4.1.
Rotary-linear transformation
Wheel
A corkscrew with a rack and pinion
mechanism
Apply
21.
Measure the back wheel of your bicycle. What is the diameter?. If the wheel
makes one rotation, how far do they move? Repeat this calculation for a
children’s bicycle with a wheel that has a diameter of 24 cm.
Analyse
22.
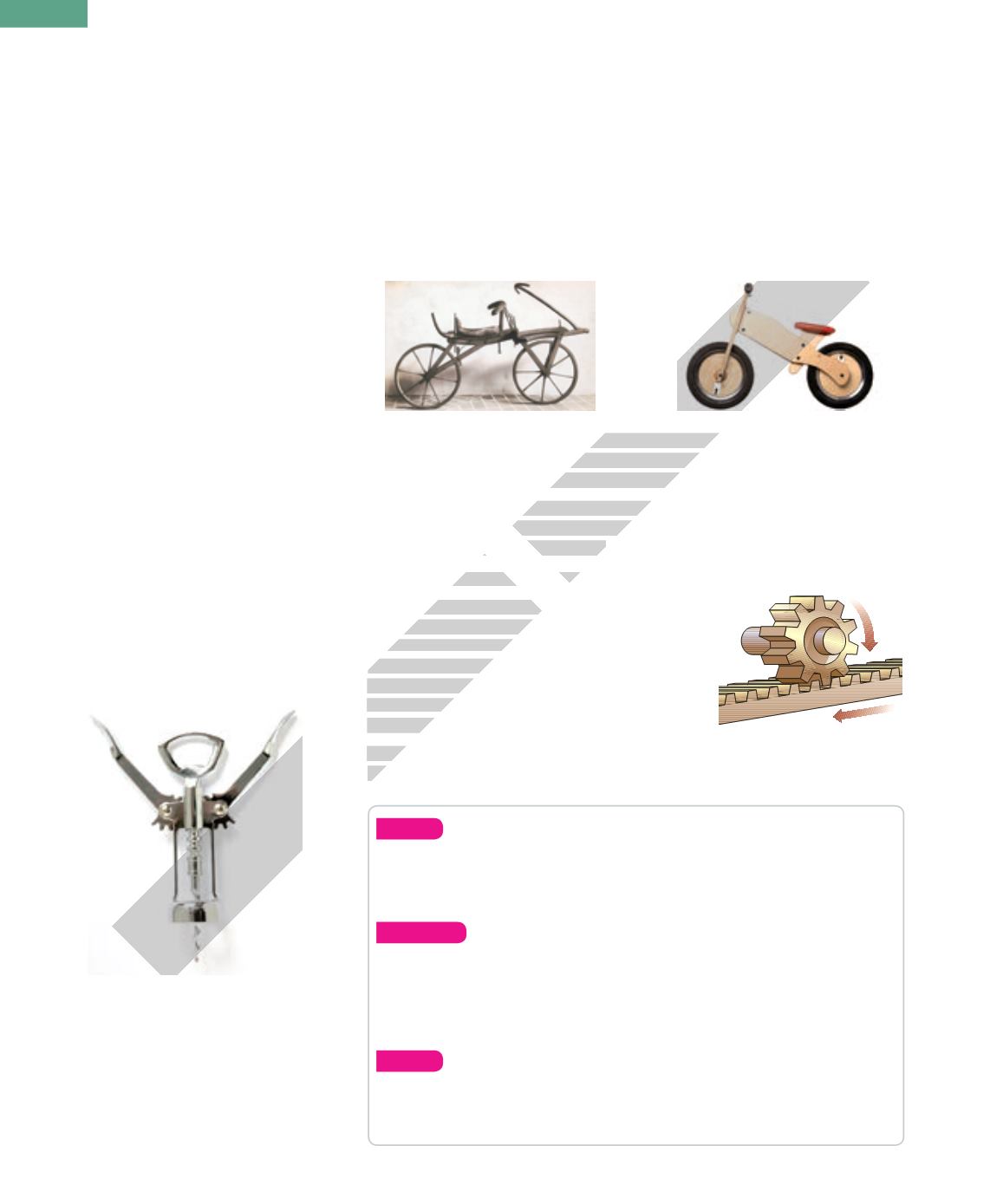
Look at the photo of the corkscrew. Locate the rack and the pinion.
Where do we apply the input force? What is the output receptor? What
work does it do?
23.
How is the rotation of a pinion related to the movement of a rack?
Apply
24.
A sliding door has got a rack and pinion system. The pinion has a radius
of 15 mm. If the door slides two metres, how many times does the
pinion rotate?
Wheels are essential parts of bicycles. They let us move more easily because they
reduce our contact with the ground and decrease friction. However, if there isn’t
enough friction, the wheels can slide out of control.
With each rotation, a wheel moves forward a distance that is equal to its
circumference (2
π
r
). As a result, we require less force to move vehicles with larger
wheels and they move more quickly.
Rack and pinion mechanism
A rack and pinion mechanism has two parts. The
rack
is a bar withmany teeth and the
pinion
is a gear
with teeth that interlock with the rack. When the
pinion rotates, the rack moves in a linear direction. If
the mechanism is reversible, the pinion also rotates
when the rack moves. Like a wheel, this mechanism
transforms rotary motion into linear motion.
Applications
:
we use rack and pinion mechanisms for sliding doors, conveyor belts
and other devices that require precise movements.
ADVANCE EDITION


