104
Apply
6.
In your exercise book, draw pictures of the levers above (seesaw,
bottle opener, tweezers) and label the fulcrum, force and resistance.
What mechanical advantage does each lever provide?
7.
Measure the handlebars of your bicycle. What is the distance from
the axis to each end? Imagine the handlebars are three times longer.
Would they be easier to turn?
Apply
3.
In this type of weighing
scales we have to move
the counterweight until
the bar balances. How
much do apples weigh
if the counterweight
balances the bar at
a distance from the
fulcrum which is six
times that of the plate.
2.
LINEAR TRANSMISSION OF MOTION
Linear transmission mechanisms, such as pulleys, use linear motion input to
produce linear motion output. We typically use these mechanisms to transmit
force.
2.1.
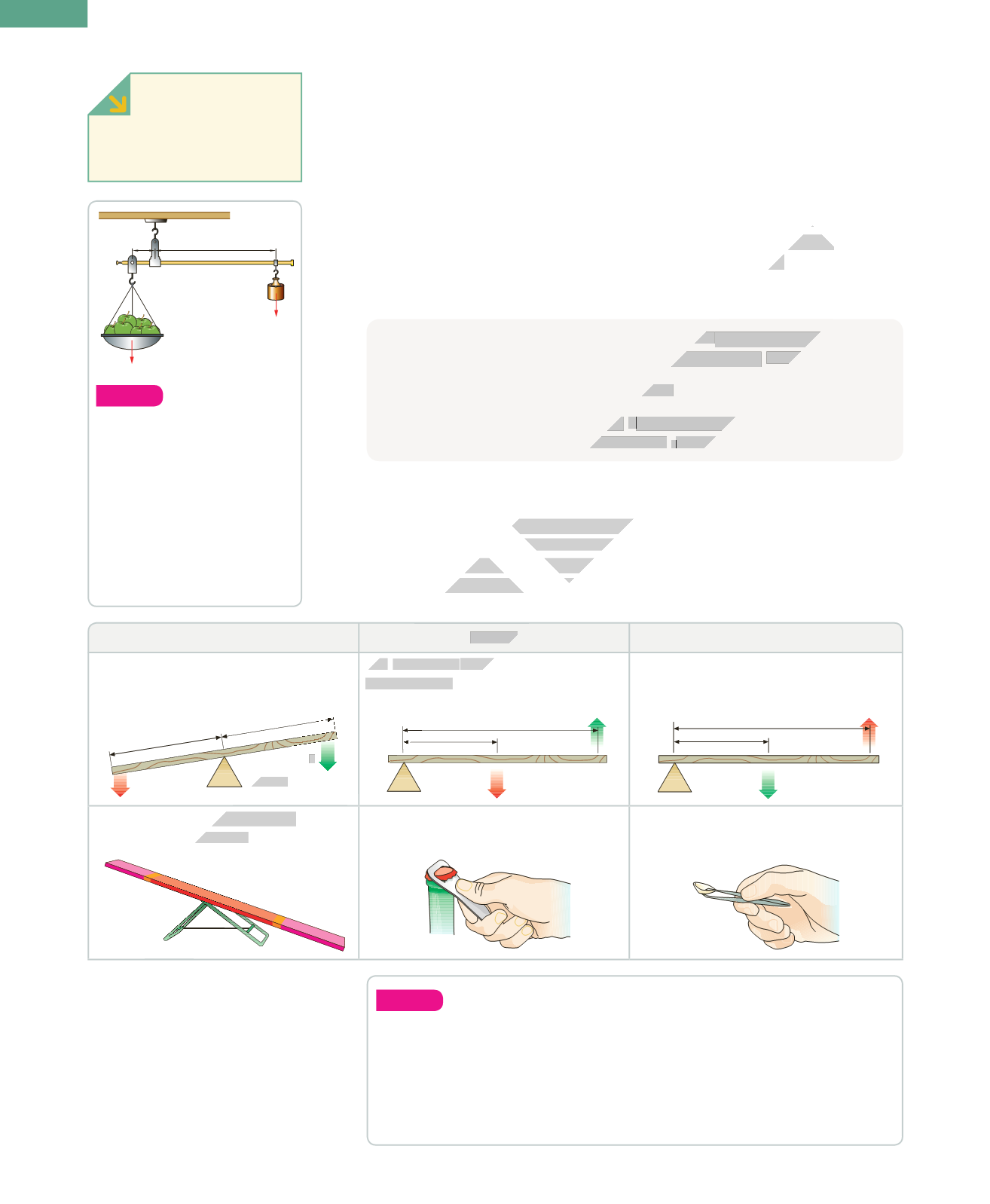
Levers
A lever is a rigid bar that turns around a point called a
fulcrum
9
. Various forces
may act on the lever at the same time. Each force produces a specific
torque
10
,
which is the force multiplied by its distance from the fulcrum. .
Torque = Force x Distance
Classes of levers
We can divide levers into classes according to the locations of the
fulcrum
,
force
and
resistance
. Each class of lever has different uses. Class 2 levers increase the force
that we apply. Class 3 levers increase the distance that the end of the lever moves.
Class 1 levers can do both of those things. We also use them to compare weights.
When the forces acting on opposite ends of a
lever
are equal, we say the lever
is in equilibrium. We can express this mathematically as the
Law of the Lever:
F · d = R · r
F
is the force or the effort that we use;
d
is its distance from the fulcrum;
R
is the
resistance or load that we want to move and
r
is its distance from the fulcrum.
Class 1
Class 2
Class 3
The
fulcrum
is between the force and
the resistance.
The
resistance
is between the fulcrum
and the force.
The
force
is between the fulcrum and
the resistance.
The effect of the force applied is
increased or decreased.
The effect of the force applied is always
increased
(d > r).
The effect of the force applied is always
decreased
( d < r).
R
F
fulcrum
r
d
R
F
fulcrum
r
d
F
R
fulcrum
d
r
d
6
d
m
= 400 g
F
1
F
2
MEASUREMENTS
In this unit, we measure force
in
newtons (N)
and distance (d,
r) in
centimetres
(cm).
9
fulcrum
: point of support for a lever
10
torque
: moment of force
ADVANCE EDITION


