1
1. The world’s natural environment
25
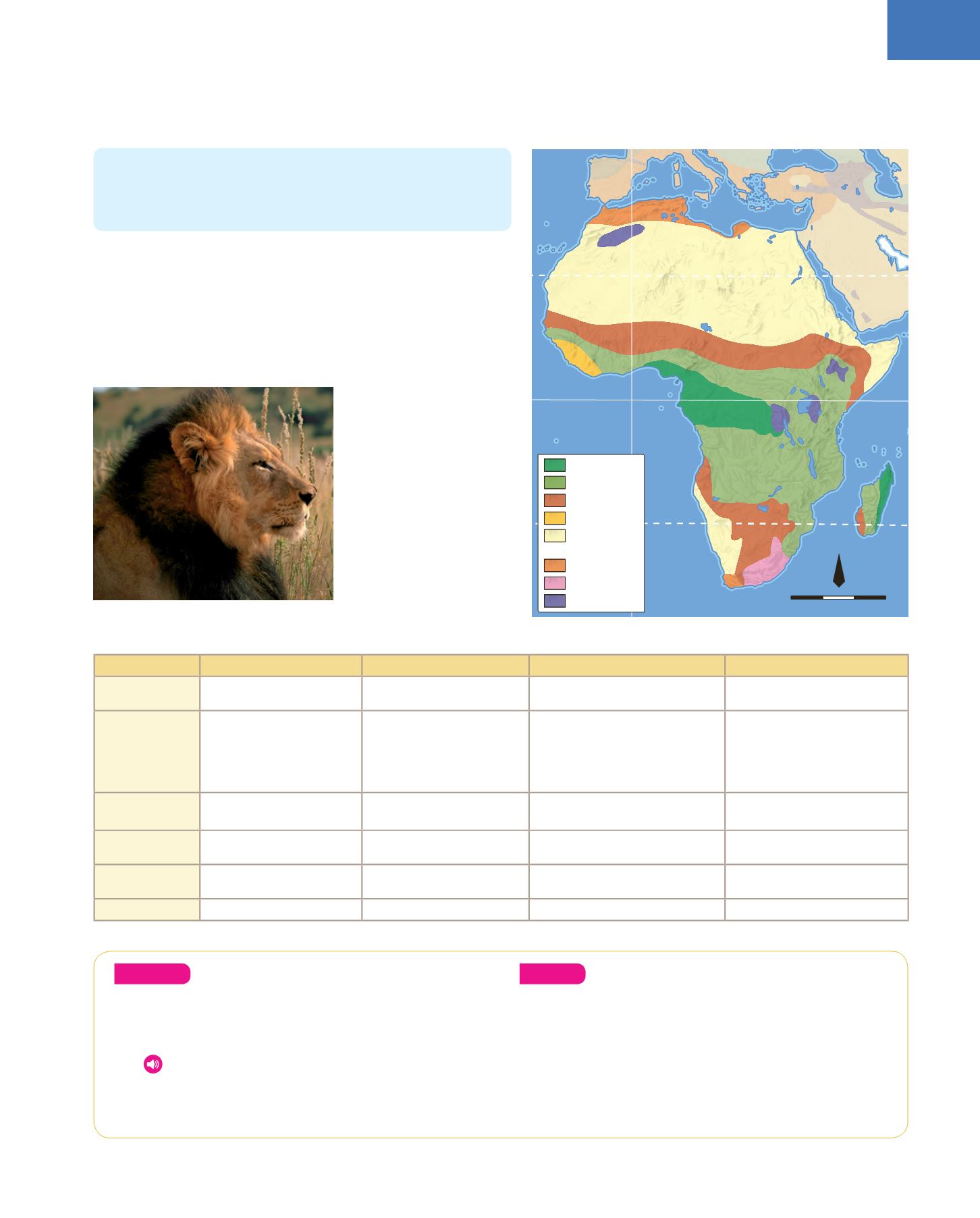
7.2. Climates and biogeography
In the centre of Africa the
equatorial
climate predominates. The wet
tropical climate (
Sudanese
) and the dry tropical climate (
Senegalese
)
extend progressively to the north and to the south. Then are the
deserts, the
Sahara
in the north (the largest in the world) and the
Kalahari
and the
Namib
to the south (originating from the cold
Benguela Current
). In the southern tip of the continent there is a
small area of
Chinese climate
.
The vegetation and fauna
are defined by the climate.
Jungle predominates in
the wet equatorial areas.
The Savannah is the typical
type of vegetation. In this
natural environment are
the greatest concentrations
of wildlife in the world,
such as lions, leopards,
elephants, rhinoceroses,
gnus, zebras, giraffes,
gazelles and hyenas.
Most of the African climates are warm (this continent lies between
the two tropics). There are also small areas with a
Mediterranean
climate
on the north coast and the extreme southwest of South
Africa, and also
mountain climates
.
Climate
Temperatures
Precipitation
Vegetation
Fauna
Equatorial
AMT >20 ºC
Small thermal range
>1500 mm
All year
Forest (trees, vines)
Gorilla, elephant, monkey
Tropical wet
Tropical dry
AMT 20-28 ºC
Small thermal range
AMT 20-28 ºC
Medium thermal range
800-1500 mm
Summer rains
300-800 mm
Clear forest and savannah
(grasses, acacias, shrubs)
Grassy and bushy savannah
Elephant, lion, leopard,
rhinoceros, hyena, zebra,
gnu,giraffe, crocodile,
hippopotamus, gazelle,
ostrich, vulture
Desert and
semi-desert
Large thermal range
<100 mm-300 mm
Cactus and thorny bushes
Fox, gazelle, dromedary
Chinese
AMT 15-25 ºC
Medium thermal range
800-1500 mm
Rains in summer
Clear forest, bushes and
scrubland
Leopard, gazelle, elephant
Mediterranean
AMT 10-20 ºC
Medium thermal range
300-700 mm
Summer drought
Forest (pine, holm oak), and
scrubland
Mountain goat, fox, birds
Mountain
Decrease with altitude
600-4000 mm
Forest and alpine meadows
Baboon, rodents
Lion
Equatorial
Tropical wet
Tropical dry
Monsoon
Desert and
semidesert
Mediterranean
Chinese
Mountain
Tropic of Cancer
Equator
Greenwich meridian
Tropic of Carpicorn
3000 km
0
1:132 181 000
N
Analyse
26.
The lakes that form part of the Rift Valley are long and
deep. Why is this? Name the most important lakes. Are
they found near volcanoes? Which ones?
27.
Look at the map on page 24 and answer the
questions.
Create
28.
Put the following animals on a blank map of Africa:
crocodile, gorilla, dromedary, zebra, and ostrich. Why
are these animals found here?
29.
On the Namib coast, the Benguela Current favours
an abundance of seals, sea lions, birds and sharks.
What is it like and where does this current come
from? Why does it favour an abundance of life?


